Photocell Wiring Diagram PDF: A Comprehensive Guide (Updated 12/17/2025)
Welcome! This guide, updated today – 12/17/2025 – provides essential photocell wiring information. Access detailed diagrams (схема) in PDF format, ensuring safe and effective installation.
Photocells, also known as photo sensors, represent a crucial safety component in automated systems, primarily utilizing infrared beams for obstacle detection. These devices are extensively employed in automatic door and gate operators, ensuring safe passage by preventing closures when an obstruction is present. Their core function revolves around adjusting electrical devices based on ambient light levels, achieved through a photosensitive resistor that alters its resistance with varying light intensity.
Understanding photocell applications necessitates recognizing their role in enhancing security and convenience. Beyond doors and gates, they feature in lighting control systems, activating lights at dusk and deactivating them at dawn. The importance of a correct photocell wiring diagram cannot be overstated, as improper connections can lead to system malfunctions or compromised safety. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of these systems, referencing available PDF documentation and schematics (схема) for accurate installation and troubleshooting. Proper installation, often exceeding 20cm in height, is vital for optimal performance.
Understanding Photocell Working Principles
Photocells operate on the principle of photo conductivity – a material’s resistance changes with light exposure. Within a photocell, a photosensitive resistor dynamically alters its electrical resistance based on the surrounding light levels. When the infrared beam between the transmitter and receiver is unobstructed, the circuit remains complete, allowing the connected device (like a gate) to function normally.
However, when an object breaks the beam, the receiver’s resistance increases, interrupting the circuit and triggering a safety response – typically halting or reversing the gate’s movement. Examining a photocell wiring diagram reveals how these components interact. The LED1 indicator, for example, signifies transmitter status; when powered, it’s off, indicating no signal transmission. Understanding these nuances, often detailed in PDF manuals and schematics (схема), is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Correct polarity and DIP switch settings (DIP1, DIP2) are also vital for proper operation, as outlined in the device’s instruction manual.
Types of Photocells Used in Wiring Diagrams
Photocell systems commonly utilize infrared (IR) technology for safety applications, frequently appearing in gate and door operator wiring diagrams. These devices consist of a transmitter and receiver pair, forming an invisible beam. Analyzing a photocell wiring diagram PDF reveals variations in connection methods, notably twist-lock configurations for secure connections.
Different models exist, some featuring adjustable sensitivity via DIP switches (DIP1, DIP2) to accommodate varying environmental conditions. The схема (schematic) within the manual illustrates these adjustments. Furthermore, some photocells incorporate cones to narrow the beam’s reception angle, enhancing precision. Understanding these distinctions is vital when interpreting wiring instructions. Installation height impacts performance; exceeding 20cm, but remaining under 2m, is generally recommended. Examining the diagram helps determine appropriate wiring for each type, ensuring correct functionality and adherence to safety standards as detailed in the product’s documentation.
120V Photocell Systems: Overview

120V photocell systems are prevalent in residential and light commercial applications, controlling lighting and security devices. A typical photocell wiring diagram PDF will illustrate the connection of the sensor to a 120V power source, a load (like a light fixture), and often a controller. These systems operate by detecting ambient light levels, activating or deactivating the connected load accordingly.
Understanding the diagram is crucial for safe installation. The neutral, line (black), and load wires are key components. Proper wiring ensures the LED indicator functions correctly – LED1 being off indicates the transmitter isn’t signaling when power is applied. Always retain the manual for future reference. Twist-lock photocell sensors are common, requiring specific wiring techniques. Referencing the схема (schematic) within the PDF is essential for correct polarity and component placement, preventing malfunctions and ensuring system reliability.
Essential Components of a Photocell System
A functional photocell system relies on several key components, detailed in a typical photocell wiring diagram PDF. The core is the photocell itself – an infrared sensor consisting of a transmitter and receiver. A 120V power source provides the necessary energy, while a receptacle facilitates connection. The load, such as a lighting fixture or gate operator, is the device controlled by the sensor.

Controllers, often incorporating DIP switches (DIP1, DIP2) for configuration, manage system behavior. Wiring necessitates appropriate connectors, like twist-lock types, for secure connections. A photocontroller acts as the central processing unit. Examining the wiring diagram reveals the importance of correct wire colors – black for line, white for neutral, and red for the load. The PDF will also illustrate LED indicators, signaling system status. Understanding each component’s role, as shown in the схема, is vital for successful installation and troubleshooting.
Photocell Sensor Wiring Diagram Basics
Understanding photocell sensor wiring diagram basics, often found in PDF manuals, is crucial for proper installation. These diagrams (схема) typically illustrate a four-wire system: Line (Black), Neutral (White), Load (Red), and Ground. The transmitter and receiver units require separate wiring connections, detailed within the photocell wiring diagram PDF.
Twist-lock connectors are frequently used for secure and weatherproof connections. The diagram will show how the photocontroller connects to both the power source and the controlled device. Pay close attention to polarity; incorrect wiring can damage the system. LED indicators (LED1) provide visual feedback on power and signal transmission. The PDF often includes troubleshooting sections, referencing the wiring for common issues. Correctly interpreting the diagram, and understanding the function of components like DIP switches (DIP1, DIP2), ensures a functional and safe setup.
Twist Lock Photocell Sensor Wiring Diagrams

Twist lock photocell sensor wiring diagrams, commonly found in PDF format, prioritize secure and weatherproof connections. These diagrams (схема) detail the four essential wires: Line (Black), Neutral (White), Load (Red), and Ground. The receiver and transmitter units each have dedicated wiring configurations, clearly illustrated in the photocell wiring diagram PDF.
The twist-lock mechanism ensures a robust connection, preventing accidental disconnections due to weather or vibration. The diagram will show the precise alignment needed for proper locking. Careful attention to wire color coding is vital; incorrect connections can lead to system malfunction. Many PDF manuals include detailed step-by-step instructions alongside the wiring schematic. Understanding the photocontroller’s role and the function of DIP switches (DIP1, DIP2) as shown in the diagram, is key to successful installation. Always refer to the manufacturer’s PDF for specific model instructions.
Wiring Diagrams for Different Photocell Configurations
Photocell wiring diagram PDFs showcase various configurations beyond standard setups. These diagrams (схема) illustrate wiring for single, dual, and multi-zone systems, each requiring unique connections. Understanding these variations is crucial for adapting to different security needs. The PDF documentation details how to wire for normally open (NO) or normally closed (NC) operation, influencing how the system responds to beam interruption.
Different photocell types – infrared, microwave, or dual-technology – also necessitate specific wiring approaches, clearly outlined in the diagrams. Advanced configurations might include connections for alarm panels, strobe lights, or remote indicators. The PDF manual will often include troubleshooting sections addressing common wiring errors. Pay close attention to polarity considerations and LED indicator functionality, as detailed in the diagram. Correctly interpreting the схема ensures optimal performance and reliability of the photocell system.
Step-by-Step Wiring Instructions for a Standard Photocell

Consult your photocell wiring diagram PDF before beginning. First, disconnect power! Identify the transmitter and receiver units. Connect the power supply wires – typically black (line) and white (neutral) – to the designated terminals on both units. Ensure secure connections, referencing the diagram (схема) for correct placement.
Next, connect the signal wires. These wires transmit the infrared beam and are crucial for system functionality. The PDF will illustrate the correct wiring for normally open (NO) or normally closed (NC) configurations. Verify the DIP switch settings (DIP1, DIP2) align with your desired operation, as shown in the diagram.
Finally, connect the output wires to your alarm panel or control system. Double-check all connections against the photocell wiring diagram PDF before restoring power. Proper wiring, guided by the схема, is essential for reliable operation.
Troubleshooting Common Photocell Wiring Issues
When facing issues, always refer to your photocell wiring diagram PDF. A frequent problem is a lack of power; verify connections and voltage. If the LED indicator (LED1) isn’t functioning as described in the PDF, check the power supply and wiring. Intermittent signals often indicate loose connections or obstructions – clean the photocell surfaces to remove dirt buildup.
Incorrect DIP switch settings (DIP1, DIP2) can cause malfunctions; consult the diagram to ensure proper configuration. If the system triggers falsely, misalignment is likely – adjust and center the units. Reversed polarity can also cause issues; review the wiring diagram PDF and correct if necessary.
For complex problems, carefully trace the wiring against the схема in the PDF, checking each connection. Remember safety first – disconnect power before troubleshooting!
Cleaning and Maintenance of Photocells

Regular cleaning is crucial for optimal photocell performance. Consult your photocell wiring diagram PDF for specific maintenance recommendations. Excessive dirt buildup significantly impacts sensitivity; clean the photocell surfaces frequently, especially in dusty environments. Use a soft, dry cloth to gently wipe the lens – avoid abrasive cleaners.
Inspect wiring connections periodically, referencing the diagram PDF to ensure secure attachments. Check for corrosion or damage to wires and replace as needed. Verify the alignment (centering) of the units; misalignment reduces effectiveness. The PDF may contain instructions for re-alignment.
Remember, a clean photocell and secure wiring, as detailed in the wiring diagram PDF, contribute to a reliable safety system. Regular maintenance prevents false triggers and ensures consistent operation. Always disconnect power before performing any maintenance!
Addressing Dirt Buildup on Photocell Surfaces
Dirt accumulation is a primary cause of photocell malfunction. Your photocell wiring diagram PDF likely emphasizes regular cleaning. If excessive dirt builds up, the sensor’s ability to detect infrared beams diminishes, leading to gate or barrier failures. Use a soft, lint-free cloth to gently wipe the lens of each photocell unit.
Avoid harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners, as these can damage the sensitive components. A slightly damp cloth (water only) can be used for stubborn grime, ensuring it’s thoroughly dried afterward. Refer to the diagram PDF for specific cleaning instructions provided by the manufacturer.
Regular inspection, guided by the wiring diagram PDF, will help identify dirt buildup before it causes issues. Consider the environment; dusty or outdoor installations require more frequent cleaning. Maintaining a clean surface ensures reliable operation and prevents unnecessary troubleshooting.
Photocell Adjustment and Centering (Alignment)
Proper alignment is crucial for photocell functionality, and your photocell wiring diagram PDF should detail the process. After installation, carefully adjust the position of each unit to ensure the infrared beam directly crosses between them. Misalignment is a common cause of operational failures.
The diagram PDF may illustrate using the adjustment screws on the photocell housing to fine-tune the beam’s direction. Some models feature a visual indicator (LED) to aid in centering. The Russian term схему refers to the schematic, which will guide you. Screw the middle part of the photocell for adjustment.
A cone-shaped accessory can reduce the acceptance angle for more precise alignment. Refer to the wiring diagram PDF for specific recommendations regarding installation height (generally between 20cm and 2m). Accurate centering, as shown in the diagram PDF, guarantees reliable detection and prevents false triggers.
Polarity Considerations in Photocell Wiring
Your photocell wiring diagram PDF will often highlight the importance of correct polarity, particularly when dealing with DC power sources. While many photocell systems operate on standard AC voltage, some components may require direct current with specific positive and negative connections.
Incorrect polarity can lead to malfunction or even damage to the photocell’s internal circuitry. The diagram PDF should clearly indicate which wire corresponds to positive (+) and negative (-) terminals. In some cases, reversing the polarity of a single pair of photo elements (as shown in a схема) can resolve detection issues.
Pay close attention to LED indicators; when power is applied, LED1 should be off, indicating the transmitter isn’t sending signals. The wiring diagram PDF will illustrate this. Always double-check connections against the schematic before energizing the system. Proper polarity ensures optimal performance and longevity of your photocell system.
LED Indicator Functionality in Photocell Circuits
Understanding LED indicator behavior is crucial when referencing your photocell wiring diagram PDF. These lights provide valuable diagnostic information about the system’s operational status. The diagram PDF should detail the meaning of each LED’s illumination or lack thereof.
For instance, as indicated in available documentation, with power applied, LED1 should typically be off, signifying the transmitter isn’t actively sending signals. If LED1 is illuminated when it shouldn’t be, it suggests a potential issue with the transmitter circuit or wiring.
Consult the wiring diagram PDF to identify other LEDs and their corresponding functions. Some systems utilize LEDs to indicate signal strength, receiver status, or fault conditions. Properly interpreting these indicators, alongside the схема, allows for efficient troubleshooting and ensures your photocell system operates correctly.
Understanding DIP Switches on Photocells (DIP1, DIP2)
DIP switches (DIP1, DIP2) on your photocell are vital for customizing system behavior. Your photocell wiring diagram PDF is essential for deciphering their functions, as configurations vary between models. These tiny switches control parameters like sensitivity, operating modes, and synchronization settings.
The diagram PDF should clearly illustrate the effect of each DIP switch position – ON or OFF. For example, altering DIP1 or DIP2 might change the detection range or adjust the timing of the safety beam. Incorrect settings can lead to false triggers or system failures.
Some diagrams (схема) may suggest experimenting with switch positions to optimize performance for specific applications. Remember to document any changes made to the DIP switch settings for future reference. Always refer to the manufacturer’s PDF for precise details and avoid guesswork when adjusting these critical components.
Safety Precautions When Wiring Photocells
Prioritize safety when working with photocells! Always disconnect power at the breaker before commencing any wiring. Your photocell wiring diagram PDF should not replace fundamental electrical safety practices. Incorrect wiring can create fire hazards or electrical shock risks.
Ensure all connections are secure and properly insulated. Use appropriate wiring gauges as specified in the diagram PDF and local electrical codes. Never work with damaged wiring or components. If you are uncomfortable with electrical work, consult a qualified electrician.
Pay close attention to polarity; reversing connections can damage the photocell. The diagram (схема) will clearly indicate correct wiring. Regularly inspect the system for wear and tear. Remember, a properly installed and maintained photocell enhances safety, but careless wiring negates these benefits. Always keep the PDF handy during maintenance!
Photocell Installation Height Recommendations
Optimal photocell installation height is crucial for reliable operation. Your photocell wiring diagram PDF won’t detail this, but it’s vital! Generally, mount units more than 20cm (approximately 8 inches) but ideally not exceeding 2 meters (around 6.5 feet). This range minimizes interference from ground obstructions and maximizes detection range.
Higher installations (up to 2m) are preferred for wider coverage areas, but consider potential signal blockage. Lower mounting can be suitable for narrow driveways, but increases susceptibility to false triggers from small objects. Refer to the specific photocell model’s manual – often available as a PDF – for precise recommendations.
Incorrect height impacts performance; too low, and it detects unwanted objects. Too high, and it misses intended targets. Proper alignment (centровка) is also key, complementing optimal height. Always consult the diagram and manual for best results.
Resources for Finding Photocell Wiring Diagram PDFs
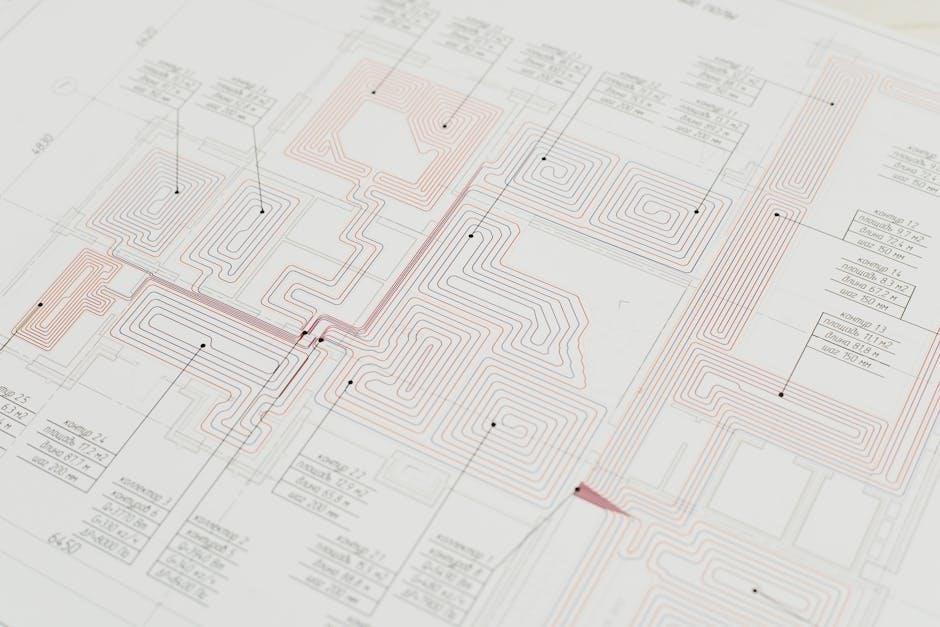
Locating a photocell wiring diagram PDF is often the first step in installation or troubleshooting. Manufacturer websites are the primary source; search directly on their support pages using the model number. Many offer downloadable manuals containing detailed schematics (схема) and wiring instructions.
Online electrical forums and communities frequently host shared PDF documents. However, verify the diagram’s accuracy against your specific photocell model. Retailer websites, like those selling automation equipment, sometimes provide diagrams as supplemental resources.
Google and other search engines are useful, but refine your search terms (e.g., “model number” + “wiring diagram” + “PDF”). Beware of unofficial sources; prioritize manufacturer-provided documentation. Remember to keep the diagram handy during the wiring process for safe and correct connections.
Interpreting Schematics (Схема) in Photocell Manuals

Photocell manuals often include schematics (схема) – visual representations of the wiring connections. Understanding these diagrams is crucial for correct installation. Key elements include identifying the power source (Line/Neutral), the load (what the photocell controls), and the sensor itself.
Pay close attention to wire colors: Black typically represents the hot wire, White the neutral, and Red often signifies the switched output. Wiring diagrams illustrate how these connect to the photocell’s terminals. Look for symbols indicating DIP switch settings (DIP1, DIP2) which affect functionality.
Trace the circuit path carefully, noting any twist-lock connections or specific polarity requirements. If the diagram is in a foreign language, use translation tools, but prioritize clarity. Always cross-reference the schematic with the manual’s written instructions for a complete understanding before beginning any wiring work.
Advanced Photocell System Configurations
Beyond standard single-photocell setups, more complex configurations offer enhanced control and security. These often involve multiple sensors working in tandem, creating a “beam break” system for gates or barriers. Advanced wiring diagrams (схема) illustrate these interconnected networks.
Consider systems utilizing both transmitter and receiver photocells, requiring precise alignment for optimal performance. These systems frequently incorporate LED indicators (LED1) to signal transmission status and potential faults. Understanding DIP switch settings (DIP1, DIP2) becomes critical for customizing sensitivity and operational modes.
Some configurations integrate photocells with existing smart home or security systems, demanding compatibility checks and potentially requiring specialized PDF documentation. Always consult detailed wiring diagrams and prioritize safety when implementing these advanced setups, ensuring proper power isolation and grounding.