Dental instruments are essential tools for diagnosis, treatment, and patient care. Knowing their names and functions ensures proper usage. They come in various types, each serving specific purposes.
Learning about dental instruments through pictures and PDF guides helps in easy identification and understanding. Regular maintenance and sterilization are crucial for longevity and patient safety.
Proper handling and care of dental instruments ensure effective treatment outcomes. Their design and materials vary, catering to different dental procedures and specialties.
Understanding dental instruments is the foundation for successful dental practice. Resources like PDF catalogs provide visual aids for identification and training purposes.
1.1. Overview of Dental Instruments
Dental instruments are specialized tools designed for various procedures, from diagnosis to treatment. They include diagnostic, restorative, surgical, and orthodontic instruments, each serving unique purposes. Understanding their functions and names is crucial for effective use. Resources like PDF guides provide detailed names, pictures, and descriptions, aiding in identification and training. These tools are essential for ensuring precise and safe dental care, making them indispensable in modern dentistry.
1.2. Importance of Knowing Dental Instrument Names
Knowing dental instrument names enhances communication among professionals, ensuring precise treatment plans. It aids in proper usage, reducing errors and improving patient safety. Familiarity with names also facilitates efficient instrument selection and maintenance. Resources like PDF guides with images and descriptions help in quick identification, making them valuable for education and practice. Accurate naming is critical for effective teamwork and optimal patient care in dentistry.
1.3. Purpose of Using Dental Instruments
Dental instruments are used for examination, diagnosis, and treatment of dental conditions. They aid in procedures like cavity preparation, gum surgery, and orthodontic adjustments. Instruments like mirrors and probes help in precise diagnostics, while others facilitate restorative and surgical tasks. Their purpose is to improve patient outcomes, ensuring safe and effective care. Resources like PDF guides provide detailed insights, helping professionals understand their use and maintenance, enhancing overall dental practice efficiency and patient satisfaction.
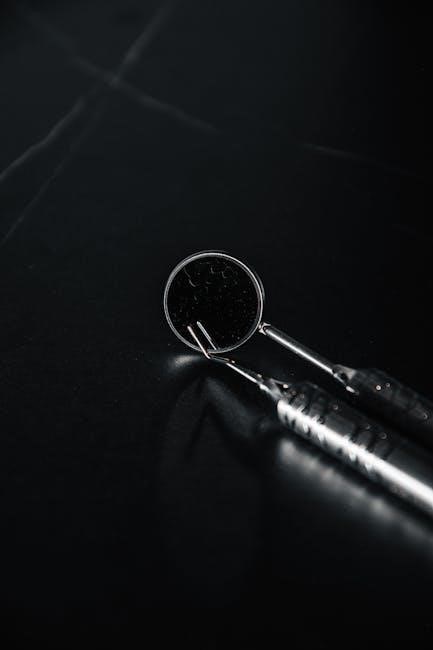

Basic Diagnostic Instruments
Basic diagnostic instruments are essential for examining and diagnosing dental conditions. Tools like dental mirrors, probes, and explorers help in precise patient assessments and effective treatment planning.
2.1. Dental Mirror
The dental mirror is a fundamental diagnostic tool used for indirect vision and illumination in the oral cavity. It helps examine areas difficult to see directly.
Front surface mirrors provide clear images, while rear surface mirrors reduce distortion. Regular cleaning with solutions like ENZYMEC ensures hygiene and clarity.
Dental mirrors are essential for precise diagnoses and effective treatment planning. Their proper use enhances patient care and procedural accuracy.
Referencing PDF guides with pictures aids in identifying and understanding dental mirrors, ensuring correct usage in clinical settings.
2.2. Periodontal Probe
The periodontal probe is a diagnostic instrument used to measure pocket depths around teeth, assessing periodontal health. It features markings at millimeter intervals for precise measurements.
Proper use involves gently inserting the probe into the gingival sulcus to determine the depth. This helps in diagnosing periodontal disease and monitoring treatment progress.
Regular cleaning with solutions like ENZYMEC ensures the probe remains free from contaminants. PDF guides with images aid in understanding its features and correct usage techniques.
The periodontal probe is indispensable for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning in periodontal care.
2.3. Explorer
The explorer is a basic diagnostic tool used to detect dental caries and irregularities on tooth surfaces. It features a thin, curved or angled probe with a sharp point.
It is gently drawn across enamel to identify changes in texture, aiding in early cavity detection. Regular cleaning with solutions like ENZYMEC ensures hygiene and longevity.
Explorers are essential for precise examination and are often illustrated in dental instrument PDF guides for easy identification and understanding of their structure and use.
The explorer’s design allows for detailed inspection, making it a cornerstone in preventive dental care and diagnostic procedures.
2.4. Tweed Mouth Mirror
The Tweed Mouth Mirror is a diagnostic tool used for indirect vision and illumination in dental procedures. It features a curved surface and a built-in light source for clear visibility.
Its design allows dentists to examine areas difficult to see directly, enhancing precision in diagnoses. Regular cleaning with solutions like ENZYMEC ensures optimal performance and hygiene.
Illustrations in dental instrument PDF guides help in identifying the Tweed Mouth Mirror, emphasizing its role in comprehensive oral examinations and treatments.
Proper maintenance and storage are crucial to extend its longevity and ensure consistent reliability in clinical settings.
Restorative Dental Instruments
Restorative dental instruments, such as excavators and burnishers, are crucial for repairing teeth. Regular sharpening and cleaning with solutions like ENZYMEC maintain their effectiveness, as detailed in PDF guides.
3.1. Dental Excavator
A dental excavator is a hand instrument used to remove decayed tooth material. It features a curved or angled blade for precise removal of caries. Available in different sizes, it ensures minimal tooth structure loss. Proper sterilization and sharpening, as outlined in maintenance guides, are essential for effectiveness. PDF resources provide detailed images and descriptions for easy identification and handling. Regular cleaning with solutions like ENZYMEC keeps them in optimal condition for procedures.
3.2. Burnisher
A burnisher is a dental instrument used to polish and smooth surfaces of restorations or tooth structures. It features rounded or flat tips made of stainless steel or other durable materials. Burnishers are essential for contouring and removing minor imperfections during restorative procedures. They are available in various shapes and sizes, each designed for specific tasks. Proper handling and sterilization, as outlined in maintenance guides, ensure longevity. Visual guides and PDF resources provide detailed images for easy identification and training.
3.3. Spatula
A spatula is a versatile dental instrument used primarily for mixing and smoothing materials like impression compounds or cements. It features a flexible, heat-resistant blade and a comfortable handle for precise control. Spatulas are essential in restorative procedures for achieving smooth surfaces. They come in different sizes and shapes to suit various applications. Proper cleaning and sterilization, as per maintenance guides, ensure durability. PDF resources and visual guides provide clear images for easy identification and handling techniques.
3.4. Amalgam Carver
The amalgam carver is a specialized dental tool used in restorative dentistry to shape and carve amalgam fillings. Its angled blade and curved or angled tips allow for precise contouring and removal of excess material. Proper handling ensures smooth adaptation of amalgam to tooth surfaces. Regular sterilization and maintenance, as outlined in dental care guides, are essential for longevity. High-quality images in PDF resources help in identifying and understanding its design and functionality.

Surgical Dental Instruments
Surgical dental instruments are specialized tools used for precise procedures. They include scalpels, forceps, retractors, and elevators, each designed for specific tasks. PDF guides provide detailed images for easy identification and understanding of their use in surgeries.
4.1. Scalpel
The scalpel is a fundamental surgical dental instrument used for precise cutting and incisions. It is commonly employed in procedures like tissue removal or biopsy. Available in various types, such as surgical and utility scalpels, they feature sharp blades attached to ergonomic handles. PDF guides and images highlight their design and proper handling techniques. Sterility and maintenance are crucial to ensure safe and effective use during dental surgeries. Proper storage and sharpening extend their lifespan and performance.
4.2. Surgical Forceps
Surgical forceps are essential tools in dental procedures, used for gripping and holding tissues or objects. They come in various types, such as needle holders and tissue forceps, each designed for specific tasks. PDF guides and images provide detailed visual aids for identification and proper handling. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and sterilization, ensures their longevity and effectiveness. Proper storage and sharpening techniques are also crucial to maintain their precision and functionality during surgical procedures.
4.3. Retractors
Retractors are dental instruments used to retract tissues, providing clear access during surgical procedures. They come in various types, such as tissue retractors and mouth retractors, each designed for specific needs. PDF guides and images help in identifying and understanding their proper use. Regular sterilization and maintenance ensure optimal performance. Proper storage and handling are crucial to extend their lifespan. Retractors play a vital role in ensuring visibility and precision during dental surgeries, making them indispensable tools in modern dentistry.
4.4. Elevators
Elevators are surgical dental instruments used to loosen and remove teeth or roots from sockets. They come in various shapes, such as Seldin or Cryer elevators, designed for specific procedures. Made from durable materials like stainless steel, they feature curved or angled tips for better leverage. PDF guides and images provide clear identification and usage examples. Regular sharpening and sterilization are essential for maintaining their effectiveness. Proper storage in sterilized containers ensures longevity and safety. Elevators are indispensable in dental surgeries for precise tooth extraction.

Orthodontic Instruments
Orthodontic instruments, like pliers and wires, are used to align teeth. PDF guides provide detailed names and images for easy identification and training purposes.
5.1. Pliers
Orthodontic pliers are essential for bending and shaping wires used in braces. They come in various types, such as needle-nose and heavy-duty pliers, each designed for specific tasks.
PDF guides and images help identify different pliers, ensuring proper selection for procedures. Their precise design enables accurate wire adjustments, crucial for effective tooth alignment.
Regular maintenance and proper storage extend the lifespan of orthodontic pliers, ensuring optimal performance in dental treatments.
5.2. Wires
Orthodontic wires are crucial for applying pressure to teeth, guiding them into proper alignment. They come in different types, such as stainless steel and nickel-titanium, each offering unique properties.
Stainless steel wires provide rigidity, while nickel-titanium wires are flexible and ideal for initial stages. PDF guides and images help in identifying wire types and their applications.
Visual resources are essential for understanding wire selection and placement, ensuring effective orthodontic treatment; Proper handling and storage of wires maintain their integrity and performance.
5.3. Bands
Orthodontic bands are metal rings fitted around teeth to anchor braces. They are commonly used on molars for added stability. Bands are made from materials like stainless steel or ceramic.
They are customized to fit individual teeth securely. PDF guides and images help in identifying different band types and their applications in treatment plans.
Proper fitting and adjustment of bands are crucial for effective orthodontic treatment. Regular maintenance ensures they remain secure and functional throughout the process.
5.4. Brackets
Orthodontic brackets are small devices attached to teeth to hold archwires. They come in metal, ceramic, or self-ligating types, each designed for specific needs and aesthetics.

Brackets are crucial for applying controlled force to align teeth. PDF guides and images provide detailed views, aiding in identification and understanding of their design and functionality.
Proper placement and adjustment of brackets are essential for effective orthodontic treatment. They are customized to fit individual tooth shapes and treatment plans.
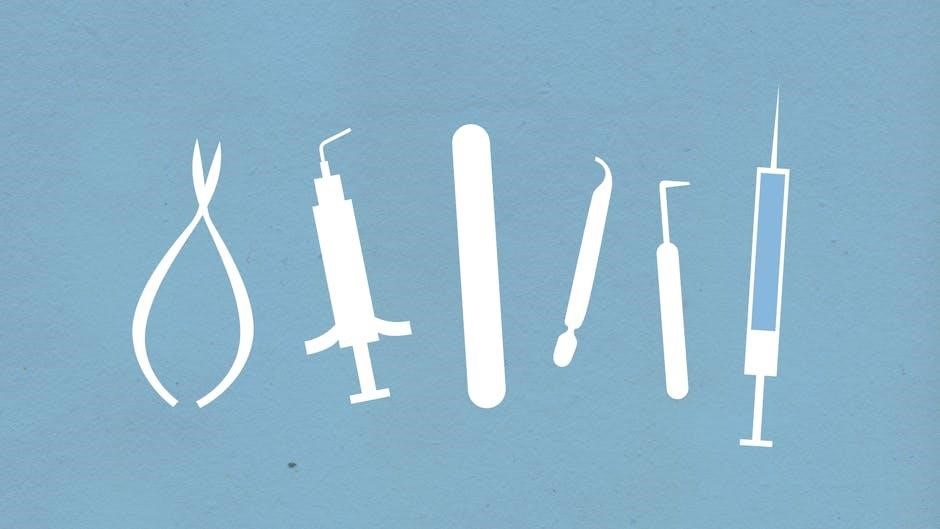
Prosthetic Dental Instruments
Prosthetic dental instruments are used to create and fit dental prosthetics. Key tools include impression trays, alginate mixers, and polishing wheels for precise fabrication and finishing.
These instruments ensure accurate impressions and smooth prosthetic surfaces, enhancing patient comfort and aesthetics. PDF guides and images provide detailed insights into their design and application.
6.1. Impressions Trays
Impression trays are crucial for capturing accurate dental impressions. They come in various sizes and types, such as stock trays and custom trays, ensuring a precise fit for each patient.
These trays are used with impression materials like alginate or silicone. Proper selection and handling are vital for achieving accurate results. PDF guides and images help in identifying and using impression trays effectively, ensuring high-quality dental restorations and prosthetics;
6.2. Alginate Mixers
Alginate mixers are essential tools for preparing dental impressions. They ensure the correct consistency of alginate material by mixing powder and water thoroughly.
Manual and automatic mixers are available, offering efficient and bubble-free mixing. Proper use of alginate mixers is crucial for accurate dental impressions, aiding in precise restorations and prosthetics.
PDF guides and images provide detailed instructions and visual aids for selecting and using alginate mixers effectively, ensuring optimal results in dental procedures.
6.3. Casting Machines
Casting machines are crucial for creating precise dental appliances like crowns and bridges. They use materials such as cobalt-chromium or titanium to produce durable restorations.
These machines often employ vacuum or pressure casting techniques to ensure accuracy. High-quality images in dental instrument PDF guides help in identifying and understanding their operation.
Regular maintenance and proper usage of casting machines are essential for consistent results, making them indispensable in modern dental laboratories.
6.4. Polishing Wheels
Polishing wheels are essential tools for refining dental restorations, ensuring a smooth surface finish. They are typically made of rubber or felt and used with polishing compounds.
These wheels are compatible with dental drills and come in various shapes and sizes for precision work. High-quality images in dental instrument PDF guides help in identifying different types.
Proper maintenance, including cleaning and replacing worn wheels, is crucial for optimal performance. They are indispensable in creating aesthetically pleasing and durable dental prosthetics.
Dental Instrument Maintenance
Regular maintenance ensures dental instruments remain functional and safe. Cleaning with agents like ENZYMEC and sterilizing are crucial steps. Proper care extends instrument longevity and prevents contamination.
Sharpening and storage solutions also play key roles in maintaining efficiency. Detailed guides and PDF resources offer visual instruction for effective instrument care and handling techniques.
7.1. Cleaning Dental Instruments
Cleaning dental instruments is a critical step in maintenance. Use enzyme-based cleaners like ENZYMEC for effective pre-cleaning. Manual scrubbing or ultrasonic devices remove residue thoroughly. Always rinse instruments with sterile water after cleaning to prevent chemical contamination. Proper cleaning ensures instruments are ready for sterilization, maintaining patient safety and instrument longevity. Regular cleaning also prevents corrosion and extends the lifespan of dental tools. Follow manufacturer guidelines for optimal results. Detailed cleaning protocols can be found in dental instrument care PDF guides.
7.2. Sterilization Methods
Sterilization of dental instruments is essential for eliminating pathogens. Autoclaving, using high-pressure steam, is the most common method. Dry heat sterilization is an alternative for non-metallic tools. Ethylene oxide sterilization is used for heat-sensitive instruments. Proper sterilization prevents cross-contamination and ensures patient safety. Always follow manufacturer guidelines and standardized protocols for effective sterilization. Regular maintenance of sterilization equipment is crucial. Refer to dental instrument care PDF guides for detailed sterilization procedures and best practices.
7.3. Sharpening Techniques
Sharpening dental instruments is crucial for maintaining their effectiveness. Manual sharpening with stones or files is common, while automated sharpeners offer precision; DENTSPLY guides recommend regular sharpening of scalers and curettes. Proper techniques prevent instrument damage and ensure sharp edges. Always follow manufacturer instructions for specific tools. Sharpening frequency depends on usage. Regular maintenance enhances instrument longevity. Refer to dental instrument care PDFs for detailed sharpening methods and best practices to ensure optimal performance and patient safety.
7.4. Storage Solutions
Proper storage of dental instruments is essential for maintaining their quality and longevity. Use protective cases or pouches to prevent damage. Autoclaving is common for sterilized tools, while dry storage is recommended for others. Label compartments for easy access. Store instruments in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Follow manufacturer guidelines for specific storage needs. Regularly inspect stored instruments for signs of wear or corrosion. Proper organization ensures safety and efficiency in dental practices.

Dental Instrument Pictures and Identification
Dental instrument pictures and PDF guides provide clear visuals for identification. High-quality images aid in recognizing tools, while detailed descriptions explain their names, uses, and proper handling techniques.
8.1. Visual Guide to Dental Instruments
A visual guide to dental instruments provides a comprehensive overview, combining high-quality images with detailed descriptions. This resource helps in identifying tools by their names, functions, and appearances. PDF formats offer accessibility, allowing easy reference on various devices. Visual guides are essential for education, training, and clinical practice, ensuring accurate instrument recognition. They often include labeled diagrams and categorizations, making complex tools understandable. This approach simplifies learning and enhances proficiency in dental instrumentation.
8.2. High-Quality Images for Recognition
High-quality images are crucial for accurate dental instrument recognition. Detailed visuals enhance understanding, showcasing instrument shapes, sizes, and unique features. Crisp, well-lit images enable professionals to identify tools confidently. PDF resources often include magnified views and labeled diagrams. These images aid in distinguishing similar instruments, ensuring proper selection for procedures. Updated galleries reflect advancements in dental technology, providing a comprehensive visual library for education and clinical reference.
8.3. PDF Resources for Instrument Identification
PDF resources provide comprehensive guides for dental instrument identification. These documents include detailed descriptions, high-resolution images, and catalogs. They cover various tools, from diagnostic to surgical instruments. PDFs like the DENTSPLY sharpening guide and ENZYMEC cleaning manual offer practical insights. Additionally, technical guides for materials like NEO Spectra ST include illustrated explanations. Such resources are invaluable for education, training, and clinical reference, ensuring accurate instrument identification and proper usage in dental practices.
8.4. Online Databases for Dental Instrument Pictures
Online databases offer extensive collections of dental instrument images, aiding in identification and education. Platforms like ENZYMEC and DENTSPLY provide detailed catalogs. These resources include high-quality pictures, descriptions, and specifications. They are invaluable for dental professionals and students, facilitating easy recognition of tools like scalpels, forceps, and retractors. Accessible anytime, these databases enhance learning and clinical preparedness, ensuring accurate instrument identification and proper usage in various dental procedures.
9.1. Summary of Key Dental Instruments
Dental instruments are categorized into diagnostic, restorative, surgical, and orthodontic tools. Each serves a specific purpose, from examining teeth to performing complex procedures. Key instruments include mirrors, probes, excavators, and scalers. Resources like PDF guides provide detailed names and images, aiding in identification and training. Proper maintenance and sterilization ensure longevity and safety. Understanding these tools is essential for effective dental care and successful treatment outcomes.
9.2. Final Thoughts on Instrument Usage
Proper usage of dental instruments is crucial for effective patient care and safety. Correct techniques ensure precise procedures, reducing risks and improving outcomes. Resources like PDF guides and high-quality images aid in understanding and mastering these tools.
9.3. Importance of Proper Instrument Care
Proper care of dental instruments is essential for maintaining their effectiveness and longevity. Regular cleaning, sterilization, and sharpening prevent contamination and ensure precise performance. Neglecting these steps can lead to instrument damage or patient safety risks. Using resources like PDF guides helps in understanding care techniques. Proper maintenance enhances instrument durability and ensures reliable outcomes in dental procedures. Prioritizing care is vital for both patient safety and the success of dental treatments.